How Long Does Low Testosterone Last?
The duration of low testosterone symptoms after starting testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) varies among individuals.
Generally, patients may begin to notice improvements within 2 weeks of starting testosterone therapy, but most men start feeling improvements around 6 weeks after beginning treatment.
By 6 to 12 weeks, more pronounced changes like enhanced sexual function, mood, and energy levels are often observed. Optimal results, including improved muscle strength and body composition, typically become evident within 3 to 6 months.
It’s important to recognize that TRT does not cure the underlying cause of low testosterone; it only alleviates the symptoms. Consequently, the duration of treatment depends on the individual’s specific condition and response to therapy. Continuous therapy may be necessary to maintain testosterone levels and symptom relief, requiring regular monitoring and adjustment by a healthcare provider.
At Evolve Wellness and Health in Denver, we help patients with their testosterone needs, ensuring they reach their health goals.
Will Low Testosterone Go Away On Its Own?

Low testosterone generally does not go away on its own if it is caused by an underlying medical condition or age-related decline. However, if it is due to reversible factors such as stress, poor diet, or lack of sleep, improving these aspects can help normalize testosterone levels.
In cases where low testosterone is a result of an underlying health issue, such as hypogonadism, obesity, or hormonal imbalances, it typically requires treatment or management of the underlying condition. Aging is also a common cause, and in these instances, testosterone levels usually do not recover naturally to the levels seen in younger men.
Lifestyle factors can significantly impact testosterone levels. Poor sleep, high stress, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle can all contribute to lower testosterone levels. Addressing these factors — by improving sleep quality, managing stress, losing weight, and increasing physical activity — can sometimes lead to improvements in testosterone levels.
Common Symptoms of Low Testosterone Levels

Lower testosterone levels can manifest in various symptoms that affect physical, emotional, and sexual health. These symptoms can be subtle and gradually develop over time. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for identifying and managing testosterone effectively.
1. Low Sex Drive (Libido)
Reduced sex drive, or decreased libido, is a prominent symptom of low testosterone. Testosterone, a key hormone in both men and women, plays a vital role in sexual arousal and desire.
When testosterone levels decline, individuals often experience a marked decrease in their interest in sexual activity. This change can be gradual and might not be immediately noticeable.
It’s important to understand that a diminished libido can also stem from various other factors, including stress, relationship issues, and other health conditions.
2. Mental Fog
Mental fog, characterized by reduced cognitive clarity and impaired concentration, is a notable symptom of low testosterone.
This cognitive impairment manifests in several ways. Individuals with low testosterone may find it challenging to concentrate, struggle with memory retention, or face difficulties in decision-making.
Unlike occasional forgetfulness or distraction, this mental fog is a persistent state that can significantly disrupt daily life. It often affects work performance, making it hard to complete tasks that require focus and mental sharpness. Moreover, it can strain personal relationships and social interactions, as individuals might find it hard to engage in conversations or recall important details.
The impact of mental fog extends beyond mere inconvenience; it can affect one’s sense of self and emotional well-being. People experiencing these symptoms might report feelings of frustration, decreased motivation, or a sense of inadequacy, further complicating the condition.
3. Increased Fatigue
When testosterone levels decrease, you may experience an intense sense of tiredness and lack of energy, which is not relieved by rest or sleep. This type of fatigue is more than just feeling sleepy; it’s a persistent sense of exhaustion that can affect motivation, mood, and daily productivity.
Unlike normal tiredness resulting from a busy day or poor sleep, the fatigue associated with low testosterone can be constant and debilitating. It may manifest as a general feeling of lethargy, reduced motivation to engage in physical activities, or difficulty in sustaining energy throughout the day. This can impact personal and professional life, making even routine tasks feel challenging.
This symptom can be subtle at first and may be mistaken for normal aging or stress. However, when accompanied by other symptoms, it warrants a medical evaluation.
4. Loss of Muscle Mass
Testosterone plays a crucial role in building and maintaining muscle. It promotes muscle protein synthesis, a process vital for muscle growth and repair. When testosterone levels drop, this synthesis decreases, leading to a reduction in muscle mass and strength. This change is often gradual and may initially go unnoticed.
Men with low testosterone typically experience a decrease in both muscle mass and strength, which can affect their physical performance and overall functionality. The loss of muscle mass isn’t just a cosmetic concern; it can have serious implications for overall health, including increased risk of falls and frailty, especially in older adults. Moreover, reduced muscle mass can affect metabolic health, as muscle tissue plays a key role in regulating blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
5. Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common symptom of low testosterone, which directly affects the role of the male sexual response. It works by stimulating the brain to produce nitric oxide, a molecule crucial for triggering the series of chemical reactions necessary for an erection.
When testosterone levels are low, these reactions may be insufficient, leading to difficulties in getting or maintaining an erection suitable for sexual activity. It’s important to note that while testosterone influences erectile function, ED can also be caused by other factors such as poor circulation, nerve damage, psychological issues, or medications.
Low testosterone-related ED is typically more prevalent in older men, as testosterone levels naturally decline with age. However, it can occur in younger men as well due to various health conditions.
6. Depression
In men with low testosterone, depression may not present in the classic sense of overwhelming sadness or crying. Instead, it often manifests as a persistent sense of emptiness, a loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities, or a general feeling of unhappiness.
These individuals might also experience low energy, a decrease in motivation, or a feeling of hopelessness. Such symptoms can significantly impair daily life, affecting relationships, work performance, and overall well-being.
It’s important to understand that this link between low testosterone and depression is more than just a coincidence. Testosterone influences brain chemicals that regulate mood, such as serotonin and dopamine. When levels of this hormone are low, these neurotransmitters may become imbalanced, leading to mood disturbances like depression.
How Do You Know For Sure That You Have Low Testosterone?
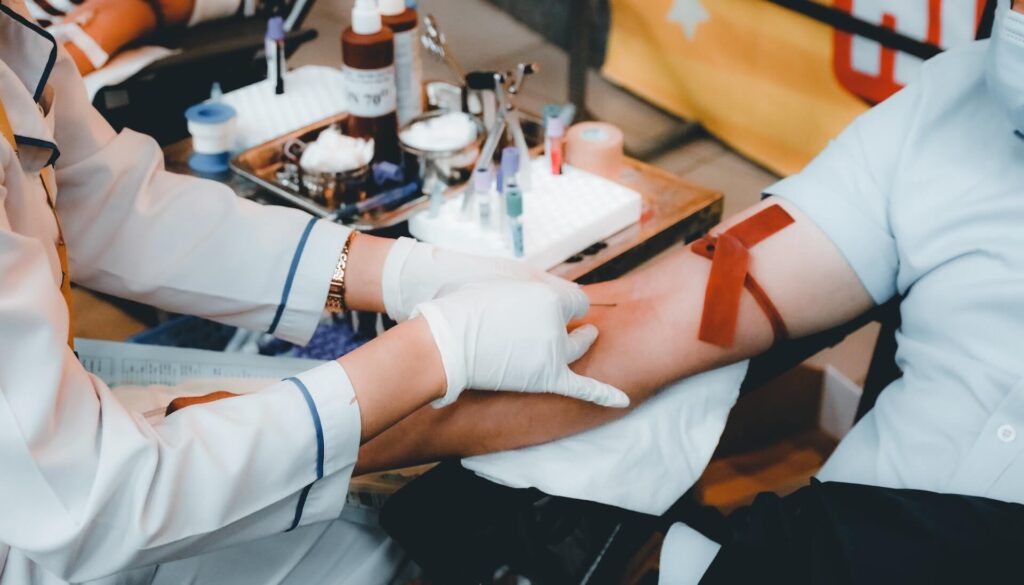
To definitively know if you have low testosterone, a medical evaluation including a blood test to measure testosterone levels is essential. Testosterone levels fluctuate throughout the day, so it’s usually best to do this test in the morning when testosterone levels are highest.
Before testing, your doctor will likely ask about symptoms associated with low testosterone. These can include reduced sex drive, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, loss of muscle mass, increased body fat, mood changes, and difficulty concentrating. It’s important to note that other conditions can also cause these symptoms, so they alone are insufficient to diagnose low testosterone.
If symptoms suggest low testosterone, your doctor will order a blood test. The normal range can vary, but it’s generally considered low if it’s below 300 nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL). However, a single low test result may not be sufficient for diagnosis. Doctors often recommend repeating the test to confirm the results, as various factors can affect testosterone levels.
Additionally, your doctor may conduct tests to determine the cause of low testosterone, such as evaluating pituitary gland function or checking for other health issues like obesity, diabetes, or hormonal disorders. A comprehensive approach ensures accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning.
Final Thoughts On Low Testosterone Recovery
In conclusion, low testosterone can manifest in various symptoms that significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. These symptoms, ranging from reduced sex drive to loss of muscle mass, highlight the hormone’s pivotal role in numerous bodily functions.
It’s essential to recognize that these symptoms can overlap with other health issues, making a definitive diagnosis challenging yet crucial. The key to addressing low testosterone lies in understanding that it’s not just a singular health issue but a multifaceted condition affecting physical, emotional, and mental well-being.
Regular medical consultations and appropriate blood tests are critical for accurate diagnosis and effective management. Treatment options, including lifestyle changes and hormone replacement therapy, can lead to significant improvements.
It’s vital for individuals experiencing these symptoms to seek medical advice, as timely intervention can not only alleviate the symptoms but also contribute to long-term health and vitality. Remember, acknowledging and addressing low testosterone can be a crucial step toward restoring balance and enhancing overall health.

Ashlee is the Medical Director at Evolve Wellness and Health in Englewood, Colorado. She obtained her Master of Science in Nursing in 2006 from Colorado State University-Pueblo, and is board-certified through the American Nurses Credentialing Center as an Acute Care Nurse Practitioner. She has practiced in the field of hormone replacement therapy (both male and female) and medical weight loss since 2013.